Antibodies
CRISPR/Cas9 antibodies
The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system uses a RNA-guided endonuclease technology which allows for inducing indel mutations, specific sequence replacements or insertions and large deletions or genomic rearrangements at any desired location in the genome. In addition, this technology, can also be used to mediate up- or downregulation of specific endogenous genes or to alter histone modifications or DNA methylation. The best characterized CRISPR-associated nucleases are the Cas9 proteins from Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. Recently two new CRISPR-associated nucleases, named Cpf1 (from Lachnospiraceae bacterium and Acidaminococcus sp.), have been described.
Diagenode, a dedicated supplier of high quality Cas9 antibodies, was the first company that offered the antibody Cas9 (clone 7A9). Diagenode now offers the largest collection of optimized anti-CRISPR/Cas antibodies, validated in a number of different applications including Western blot (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), immunoprecipitation (IP), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP).
Four critical reasons to use anti-CRISPR/Cas9 antibodies
CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing allows for double-stranded DNA breaks at specific sequences to efficiently disrupt, excise, mutate, insert, or replace genes. The precision of transfection and the level of Cas9 expression should be controlled during the editing processes using specific anti-CRISPR/Cas9 antibodies.
Reason #1 Check the transfection success of the Cas9 protein
Check Cas9 expression level using Western blot with validated anti-Cas9 antibodies.
Reason #2 Check that the Cas9 protein was delivered to the nucleus
Determine the nuclear localization of Cas9 protein via IF or IHC using validated anti-Cas9 antibodies
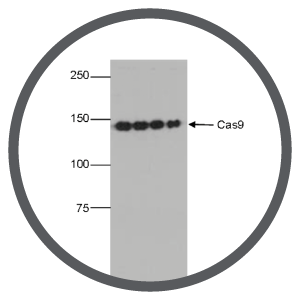
Reason #3 Check the Cas9 expression level
Transient systems: Check that Cas9 expression was transient by using Western blot and anti-Cas9 antibodies. Prolonged Cas9 expression will lead to more off-target mutations.
Stable transformants: Isolate several clones and screen to check the level of Cas9 expression using Western blot and specific anti-Cas9 antibodies. High level of Cas9 expression can lead to non-specific activity.
Reason #4 Check the binding specificity of Cas9
Test the binding specificity with an sgRNA of choice by using the ChIP-grade anti-Cas9 antibody and the primers for targeted and non-targeted region to see if Cas9 is bound to the correct region.
For more details go to the page Selection of guide RNA by ChIP.
Published examples of the use of anti-Cas9 antibodies:
- A geminivirus-based guide RNA delivery system for CRISPR/Cas9 mediated plant genome editing
- A localized nucleolar DNA damage response facilitates recruitment of the homology-directed repair machinery independent of cell cycle stage
- Rapid and highly efficient mammalian cell engineering via Cas9 protein transfection
- Use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system as an intracellular defense against HIV-1 infection in human cells
- Genome-wide CRISPR screen in a mouse model of tumor growth and metastasis
- An inducible lentiviral guide RNA platform enables the identification of tumor-essential genes and tumor-promoting mutations in vivo
